Both - they have a very limited life span, die in their droves during solar storms, and because of being so low and having no way to be recovered, their deorbiting into the upper atmosphere is going to cause massive damage to the ozone layer over the next 30 years.
Forecasts point to future reentry rates of 800–3,200 metric tons per year for satellites, and up to 1,000 metric tons per year for launch vehicles (Organski et al., 2020). The engineering approach of design-for-demise (Kärräng et al., 2019; Waswa & Hoffman, 2012) and the deployment of active debris removal solutions may further exacerbate the aforementioned trend. As for natural sources, meteoroids enter the atmosphere at an average rate of over 11,750 metric tons per year (Drolshagen et al., 2017).
Meteoriods cause 11,750 metric tons…and this papers estimate is 800-3200 tons… I think you’re reading to much into that paper.
I think you didn’t read that paper at all. It’s not just about mass, it’s about size of object, reentry angle, and the enduring quantity of particalized aluminium that stays in the upper atmosphere. Specifically that these satellite deorbits are predicted to raise that amount over the naturally occurring level by several hundred percent. That’s very much like saying “but volcanoes make co2!” - yeah, but adding a bunch of extra on top doesn’t mean the system will automatically remain stable.
That’s not how that works at all, we’ve been launching shit into space for decades now and tons of it returns, these sats from starlink are not magically going to create more than what the natual amount is showing up via meteoroids are. On top of that their estimates have a huge deviation, 800 vs 3200 is not exactly accurate.
That’s not how what works? Lumps of rock of varied composition burning up aren’t going to produce the same effects, gram for gram, as lumps of a majority of high-purity aluminium. There is little evidence that meteorites produce specifically high levels of aluminium oxide particles when entering the atmosphere (at least that I can find, I’m not dogmatic about this, I just can’t find any actual evidence that disproves this idea. I wouldn’t mind being wrong!)
Even the base estimates seem to suggest that the AlO particles will remain in the upper atmosphere for decades. AlO is proven to be a catalyst for ozone depletion, there’s quite a lot of research about that in relation to rocket exhaust gas.
The numbers of launches, satellites, and deorbits are rising pretty rapidly, so “launching shit for decades” doesn’t really mean as much as you think -
Both - they have a very limited life span, die in their droves during solar storms, and because of being so low and having no way to be recovered, their deorbiting into the upper atmosphere is going to cause massive damage to the ozone layer over the next 30 years.
Here’s a decent article - https://www.sciencealert.com/satellites-like-starlink-could-pose-new-threat-to-our-healing-ozone-layer
And the study it’s based on - https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2024GL109280
Meteoriods cause 11,750 metric tons…and this papers estimate is 800-3200 tons… I think you’re reading to much into that paper.
I think you didn’t read that paper at all. It’s not just about mass, it’s about size of object, reentry angle, and the enduring quantity of particalized aluminium that stays in the upper atmosphere. Specifically that these satellite deorbits are predicted to raise that amount over the naturally occurring level by several hundred percent. That’s very much like saying “but volcanoes make co2!” - yeah, but adding a bunch of extra on top doesn’t mean the system will automatically remain stable.
That’s not how that works at all, we’ve been launching shit into space for decades now and tons of it returns, these sats from starlink are not magically going to create more than what the natual amount is showing up via meteoroids are. On top of that their estimates have a huge deviation, 800 vs 3200 is not exactly accurate.
That’s not how what works? Lumps of rock of varied composition burning up aren’t going to produce the same effects, gram for gram, as lumps of a majority of high-purity aluminium. There is little evidence that meteorites produce specifically high levels of aluminium oxide particles when entering the atmosphere (at least that I can find, I’m not dogmatic about this, I just can’t find any actual evidence that disproves this idea. I wouldn’t mind being wrong!) Even the base estimates seem to suggest that the AlO particles will remain in the upper atmosphere for decades. AlO is proven to be a catalyst for ozone depletion, there’s quite a lot of research about that in relation to rocket exhaust gas.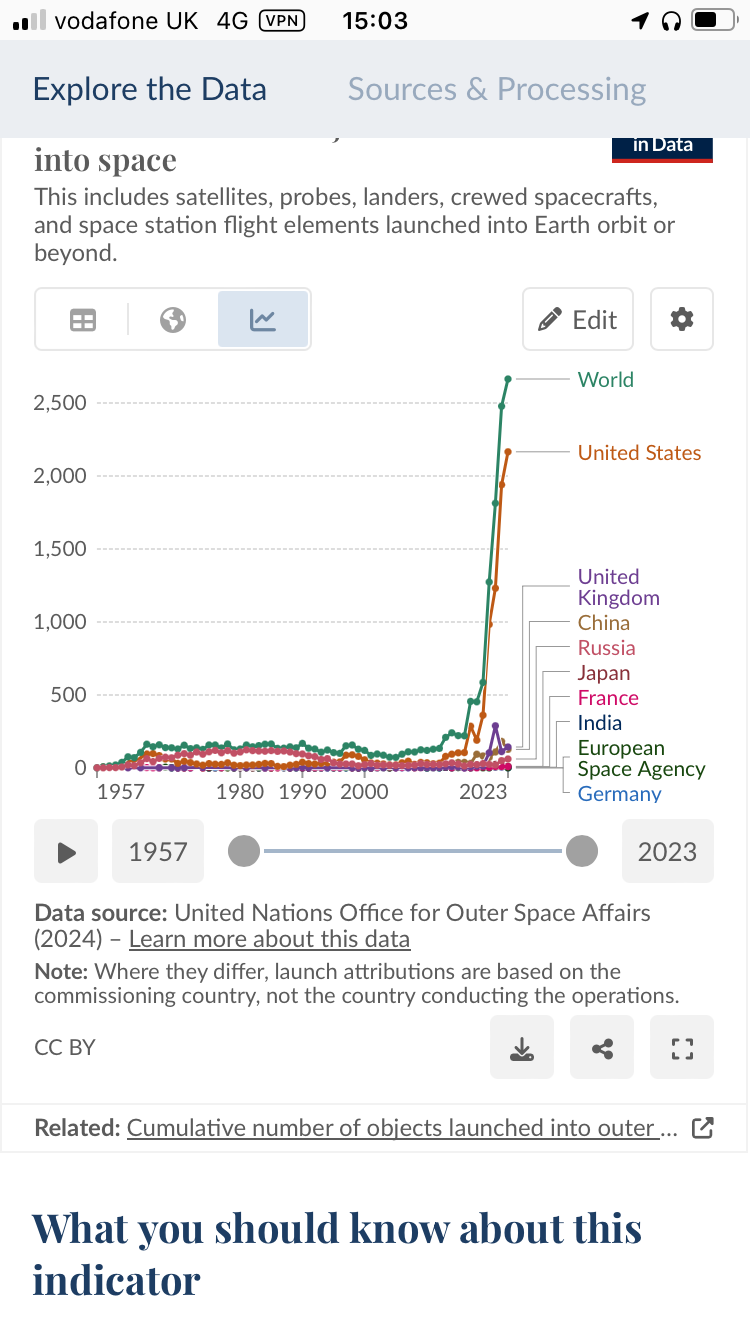
The numbers of launches, satellites, and deorbits are rising pretty rapidly, so “launching shit for decades” doesn’t really mean as much as you think -
I was pulling the number from your own paper you presented…so is your paper wrong then?