It’s worth bumping the priority up. I’m usually not that big on slice of life, but Machikado Mazoku is great.
cacheson
- 33 Posts
- 453 Comments
Don’t give your coins to politicians, kids. They’ll just become dependent and less able to survive in the wild.

 82·6 months ago
82·6 months agoPersonally, I’ve yet to see a single American successfully use guns to protect any other constitutional right from government infringement.
The Battle of Athens is probably the most uniquely clear-cut example of what you’re asking for, unless we count the American Revolutionary War itself.
Other successful examples mostly involve activists using non-violent protest to push for change, while using firearms to protect themselves from violent reactionaries that would otherwise murder them. Notably, the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 60s. For a modern example, there’s various “John Brown Gun Clubs” and other community defense organizations providing security at LGBTQ events against fascist groups that seek to terrorize event-goers.
It’s also worth noting that resistance is often worthwhile even if it doesn’t result in unqualified victory. For example, the Black Panthers’ armed cop-watching activities saved a lot of Black folks from brutal beatings at the hands of the police, even if the organization was eventually crushed by the federal government.
I have seen lots of examples like Waco and Ruby Ridge, where the government should have tried harder to deescalate, but in the end, everyone died. The closest example I can think of where the government did backoff was the Bundy standoff and all those guys were “defending” was their ability to let their cattle graze illegally on federal land because they didn’t want to pay for access like everyone else.
It sounds like you might be in a bit of a filter-bubble. I don’t mean any offense by this, it’s a normal thing that tends to happen to people. If the news sources you read and the people you talk to don’t mention these things because it doesn’t mesh with their worldview, how would you hear about them?

 1913·6 months ago
1913·6 months agoStrong gun control requires a police state, and it’s advocates are okay with this. Some of them (mostly suburbanites and the like) just imagine that that police state will never be directed against them.
Others are capitalists that actively want to inflict a police state on the rest of us, for their own benefit. It’s a lot easier to break strikes and enforce “work discipline” when the working class is disarmed.
“Clever” troll is still obvious

 1·6 months ago
1·6 months agoFood Courts Martial

 1·7 months ago
1·7 months agoHow big is a Bitcoin transaction anyway?
Bitcoin block 841,308 (most recent as I’m writing this) is 1,615,771 bytes and has 3,148 transactions, for an average transaction size of ~513 bytes.
Because a Monero transaction is about one and a half to two kilobytes
So yeah, about 3 to 4 times as large as an average Bitcoin transaction.
Keep in mind we have dynamic block scaling so that the blocks will get larger as more transactions come in.
That’s not a scaling solution, though. Larger blocks provide throughput at the expense of decentralization, since fewer people will run full nodes as resource usage increases. Eventually it gets to the point where it becomes feasible for a government to track down and compromise all the remaining node operators.
It seems like lightning service providers may very well be considered money transmitters
Not sure how much this would matter. Lightning wallets don’t care whether their channel partners are registered money transmitters, or just some rando operating through TOR or in a permissive jurisdiction. In the case of Samourai, taking down the backend rendered the wallet useless. Taking out a lightning node just temporarily inconveniences users that were connected to them.

 1·7 months ago
1·7 months agoMonero may be a good option for some individual users right now, but it isn’t a long-term solution for bringing financial privacy to the masses. That pretty much has to be done through Bitcoin wallets with privacy features. Bitcoin is already criticized for not scaling well, but Monero is far worse. If I remember correctly, Monero transactions are roughly 4 times as large as Bitcoin transactions, and they don’t have any way to do off-chain transactions the way Bitcoin can with Lightning.

 3·7 months ago
3·7 months agoYes, I agree.

 3·7 months ago
3·7 months agoDoesn’t really have anything to do with the public ledger aspect. They got busted because they were maintaining a backend service that their wallet was dependent on, and they were making money from it. Simply releasing a wallet with privacy features is still presumably legal (IANAL) due to free speech protections applying to code. The government can still prosecute end-users directly, but the same is true for users of dedicated privacy coins.

 2·7 months ago
2·7 months agoAre there any physical obstructions between the controller and the antenna? That’d reduce the effective range.

 1·9 months ago
1·9 months agoI think it’s actually a pretty old term. Definitely useful for the internet era though, now that we end up coming into contact with many more “interesting” characters than in the old days. xD

 1·9 months ago
1·9 months agoPossibly. I’ve seen comments from them here and there in various places, but it’s true that I haven’t had the responsibility of moderating them like you have.

 2·9 months ago
2·9 months agoHardlightCereal seemed more like a crank than a troll, to me. Cranks are by definition at least somewhat annoying, and tend to get mistaken for and treated as trolls. They’re not malicious the way trolls are though, and can be a positive influence. I think them drawing attention to this particular issue was a good thing, at least.
Ancaps: Government is bad because tyranny, we should get rid of it.
Also Ancaps: Here’s how we can still enforce copyright, abortion bans, and racial segregation without a government! 🥰
Nim
Part 1 was just a simple search. Part 2 looked like it just needed a trivial modification, but with the removal of the one-way tiles, the result I was getting was getting for the example was too large. I switched to a different method of determining the path length, but didn’t yet figure out what what I had been doing wrong. Since the search space was now significantly larger, my part 2 code took almost an hour to come up with the answer.
I rewrote part 2 to simplify the maze into a graph with a node for each intersection and for the start and goal tiles, with edge costs equal to the path length between each. This resulted in significantly faster iteration (17 seconds instead of 52 minutes), but didn’t actually reduce the search space. I’m assuming there’s some clever optimization that can be done here, but I’m not sure what it is.
The rewrite was still getting the wrong answer, though. I eventually figured out that it was including paths that didn’t actually reach the goal, as long as they didn’t revisit any nodes. I changed my recursive search function to return a large negative result at dead ends, which fixed the issue.
Nim
I sorted the bricks by their lower Z coordinate, then tried to move each of them downward, doing collision checks against all the others along the way. Once a level with collisions was found, I recorded each colliding brick as a supporter of the falling brick.
For part 1, I made another table of which other bricks each brick was supporting. Any bricks that weren’t the sole support for any other bricks were counted as safe to disintegrate.
For part 2, I sorted the bricks again after applying gravity. For each brick, I included it in a set of bricks that would fall if it were removed, then checked the others further down the list to see if they had any non-falling supporters. Those that didn’t would be added to the falling set.
Initially I was getting an answer for part 2 that was too high. I turned out that I was counting bricks that were on the ground as being unsupported, so some of them were getting included in the falling sets for their neighbors. Adding a z-level check fixed this.
Both of these have room for optimization, but non-debug builds run 0.5s and 1.0s respectively, so I didn’t feel the need to write an octree implementation or anything.
Nim
My part 2 solution assumes the input has an unimpeded shortest path from the center of each garden section to its corner, and to the center of its neighbor. The possible destinations will form a diamond pattern, with “radius” equal to the number of steps. I broke down the possible section permutations:
-
Sections that are completely within the interior of the diamond
- Even number of sections away from the starting section
- Odd number of sections away from the starting section
-
Sections containing the points of the diamond
-
Depending on the number of steps, there may be sections adjacent to the point sections, that have two corners outside of the diamond
-
Edge sections. These will form a zig-zag pattern to cover the diamond boundary.
- “Near” edge sections. These are the parts of the zig-zag nearer to the center of the diamond.
- “Far” edge sections. These won’t occur if the edge of the diamond passes perfectly through the corners of the near edge sections.
I determined how many of each of these should be present based on the number of steps, used my code from part 1 to get a destination count for each type, and then added them all up.
-
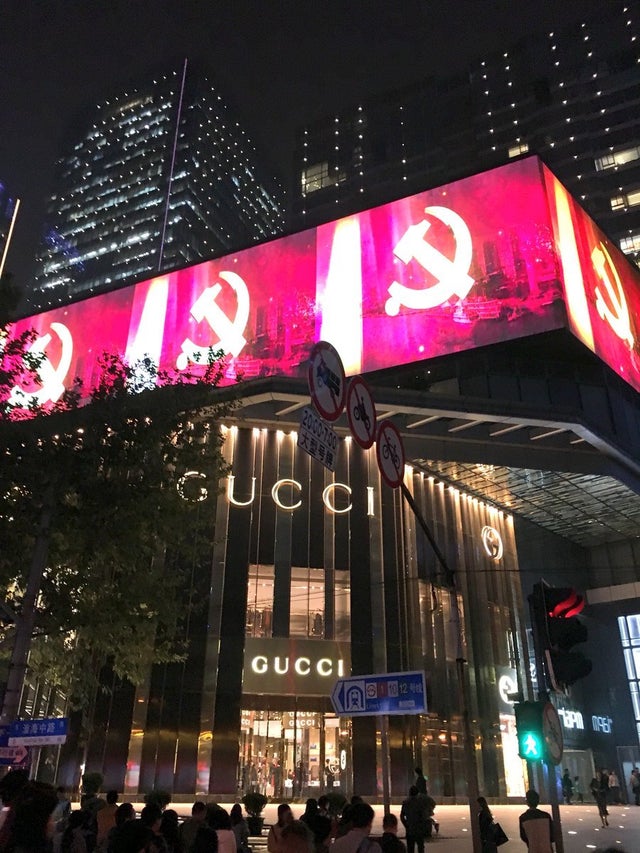





















Fellas, is it woke for YouTube to funnel viewers towards pro-fascist videos?